All Stories
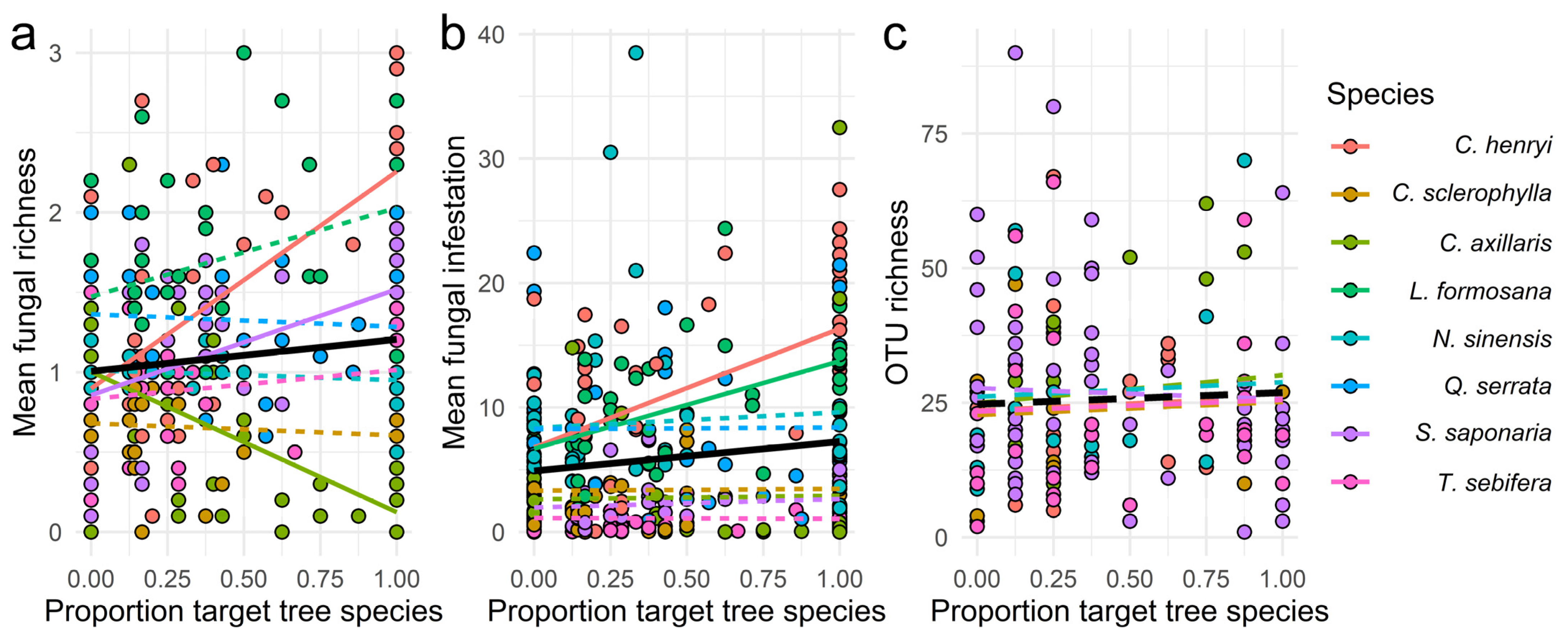
Local Tree Diversity Suppresses Foliar Fungal Infestation and Decreases Morphological but Not Molecular Richness in a Young Subtropical Forest
Leaf fungal pathogens alter their host species’ performance and, thus, changes in fungal species composition can translate into effects at the tree community scale. Conversely, the fu...
In Paper, Jul 31, 2021Species identity and composition effects on community productivity in a subtropical forest
Biodiversity experiments have shown that high species richness increases productivity in forests. However, forests are diverse regarding community composition. It is unclear how speci...
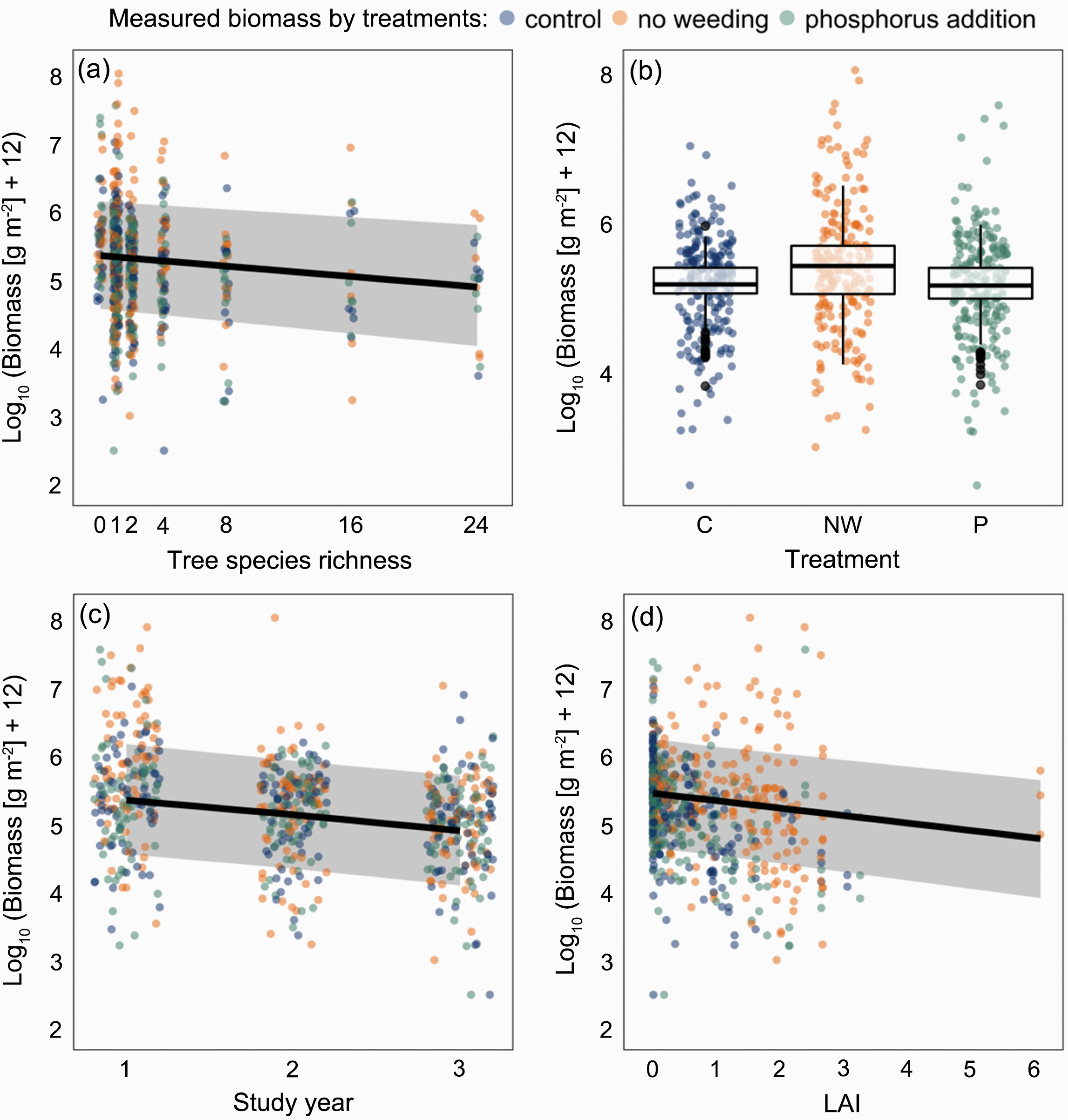
In Paper, Mar 22, 2021Drivers of understorey biomass: tree species identity is more important than richness in a young forest
Aims Positive biodiversity–ecosystem functioning relationships have been widely reported, predominately from grassland ecosystems. However, this does not necessarily have to apply acc...
In Paper, Mar 07, 2021Canopy Closure Retards Fine Wood Decomposition in Subtropical Regenerating Forests
Wood decomposition is faster in open habitats than closed-canopy forests, with the mechanisms unclear. When allowing access, termites outcompete fungi during wood decomposition. If in...
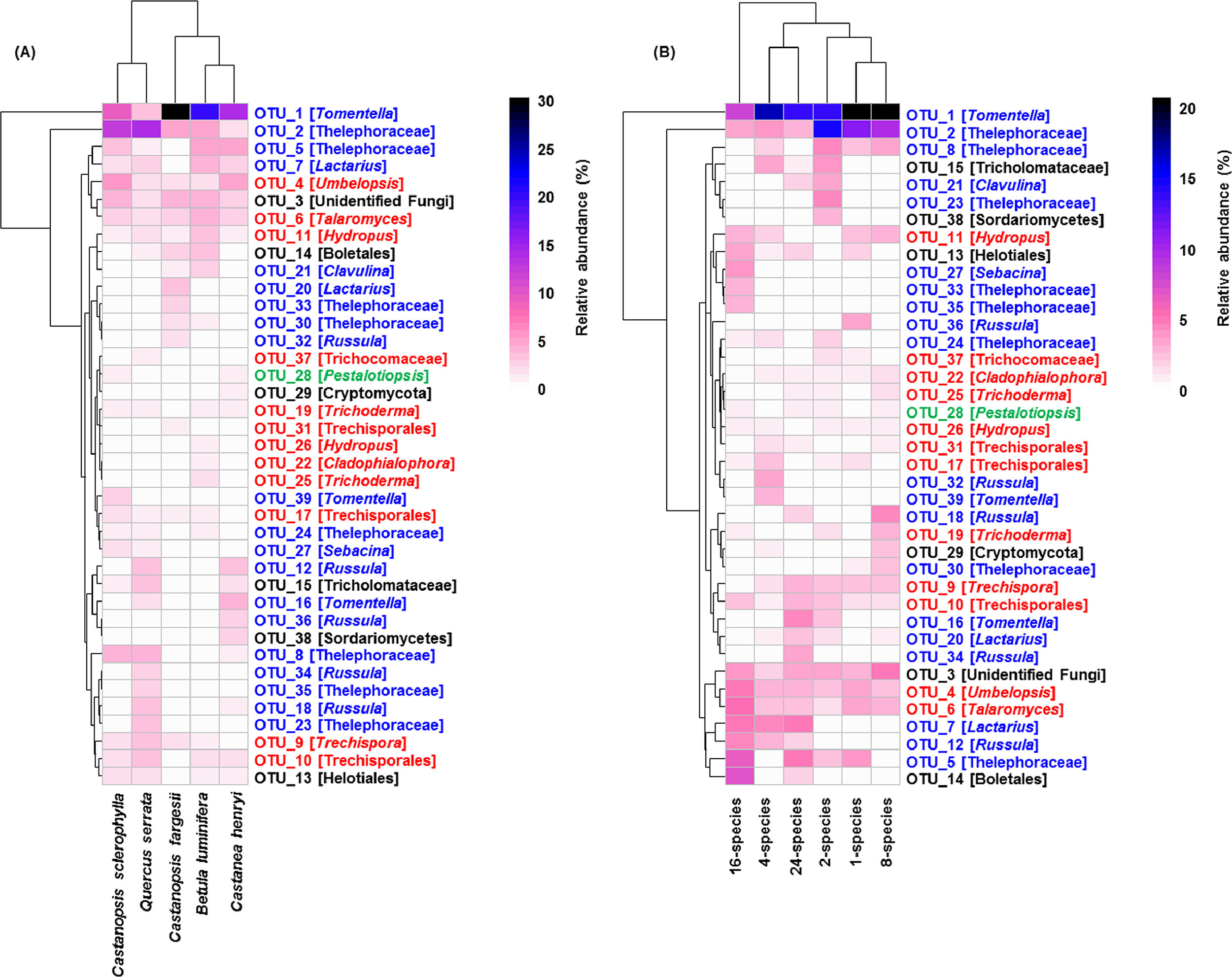
In Paper, Mar 06, 2021Plant identity strongly structures the root-associated fungal community in a diverse subtropical forest
Revealing the relationship between plants and root-associated fungi is very important in understanding diversity maintenance and community assembly in ecosystems. However, the communi...
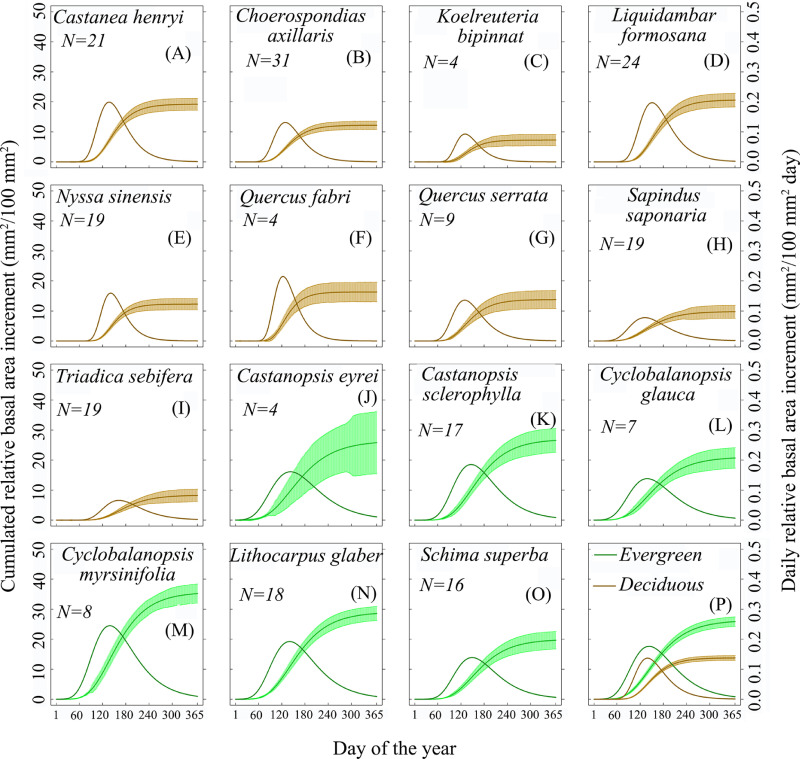
In Paper, Mar 05, 2021Radial growth response of trees to seasonal soil humidity in a subtropical forest
Tree growth is the most important factor in determining the carbon sequestration processes of forest ecosystems. However,the growth phenology (seasonal growth pattern) and responses o...
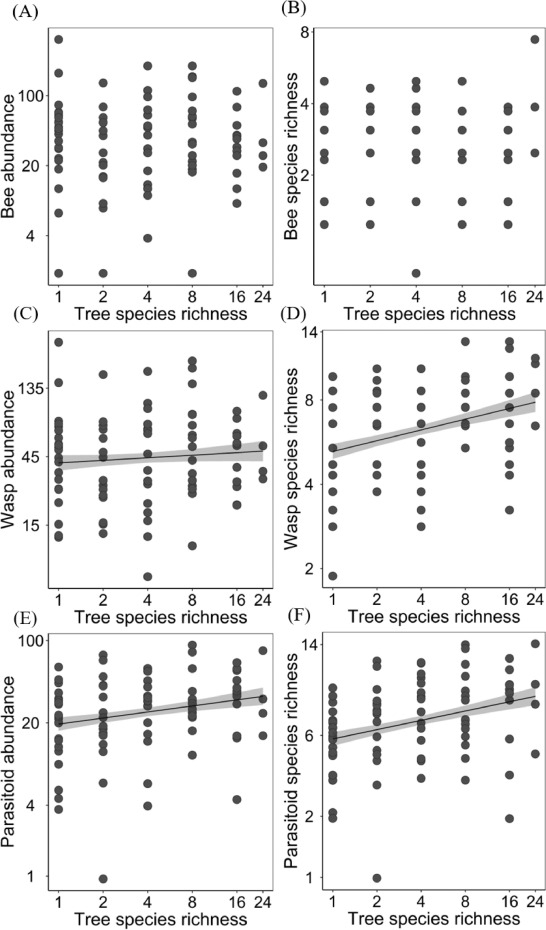
In Paper, Mar 04, 2021Tree diversity promotes predatory wasps and parasitoids but not pollinator bees in a subtropical experimental forest
From regional to global scales, anthropogenic environmental change is causing biodiversity loss and reducing ecosystem functionality. Previous studies have investigated the relationsh...
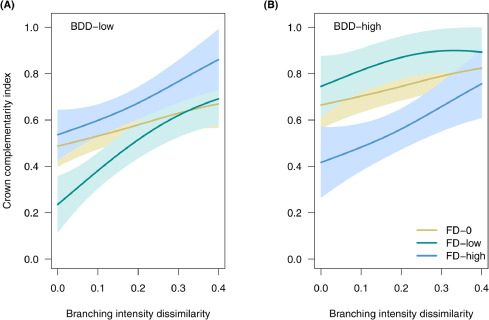
In Paper, Mar 03, 2021Tree-tree interactions and crown complementarity: The role of functional diversity and branch traits for canopy packing
Previous studies have shown that tree species richness increases forest productivity by allowing for greater spatial complementarity of tree crowns (crown complementarity), which in t...
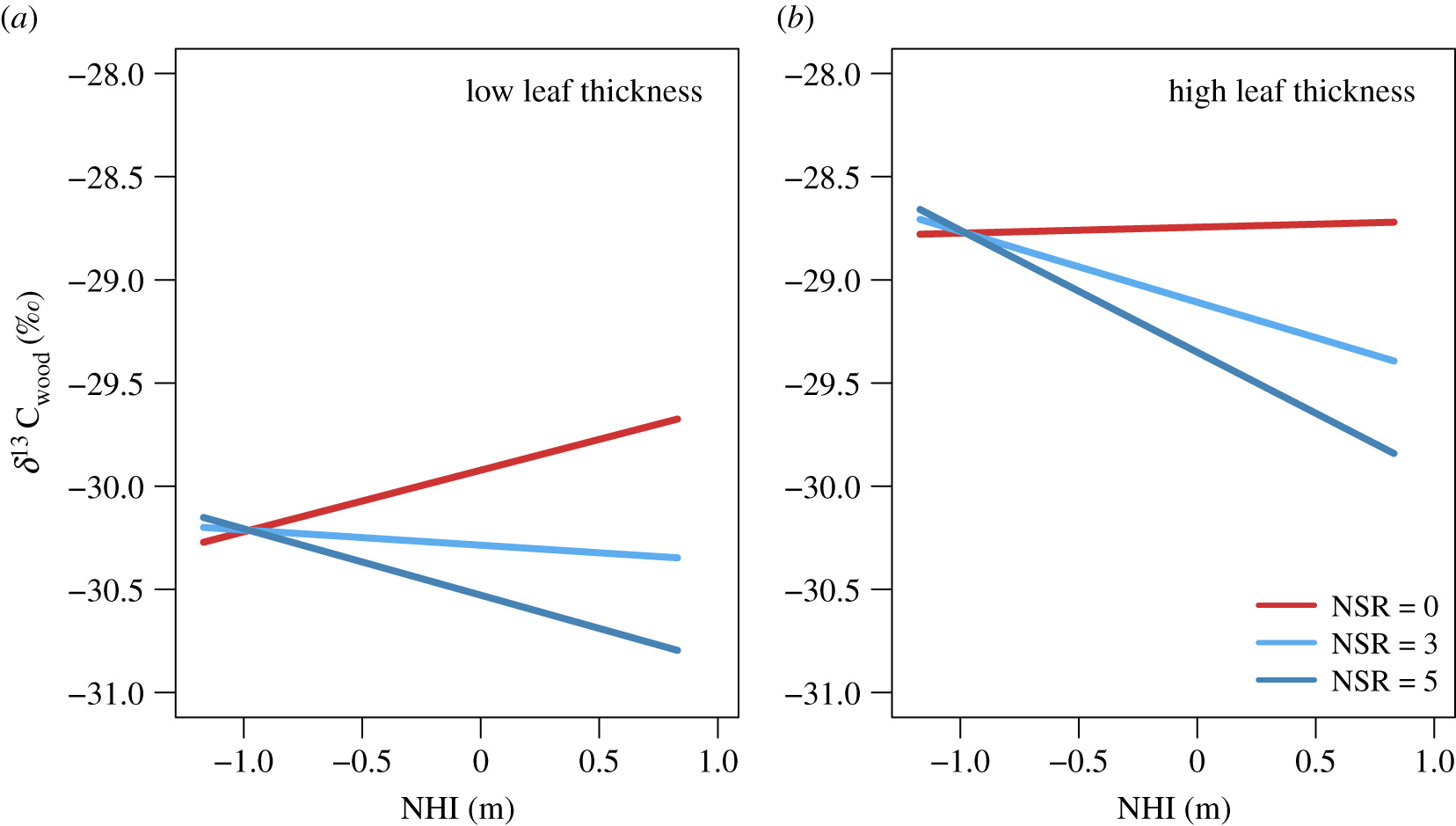
In Paper, Feb 15, 2021Tree species richness modulates water supply in the local tree neighbourhood: evidence from wood δ13C signatures in a large-scale forest experiment
Biodiversity is considered to mitigate the adverse effects of changing precipitation patterns. However, our understanding of how tree diversity at the local neighbourhood scale modula...
In Paper, Feb 05, 20219 PhD positions in forest biodiversity research within the International Research Training Group TreeDì (GRK 2324)
The International Research Training Group “TreeDì – Tree Diversity Interactions: The role of tree-tree interactions in local neighborhoods in Chinese subtropical forests” (GRK 2324), ...
In News, Jan 12, 2021Featured
-
Asynchrony and functional diversity couple herbivore community dynamics to host plant diversity
In Paper, -
Ecological insights from three decades of forest biodiversity experiments
In Paper, -
Tree species richness drives multiple facets of bee diversity via understorey microenvironment
In Paper, -
Intraspecific and intraindividual trait variability decrease with tree richness in a subtropical tree biodiversity experiment
In Paper, -
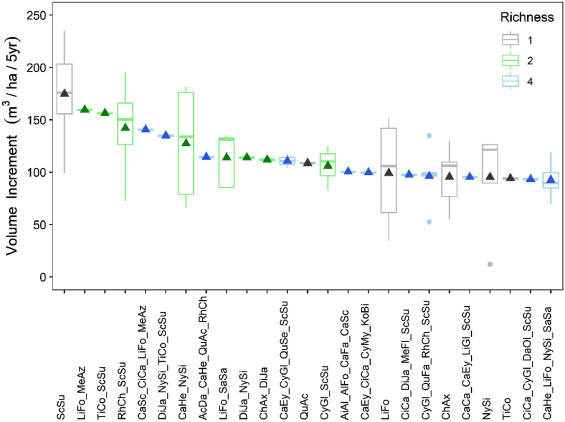
Forest biodiversity increases productivity via complementarity from greater canopy structural complexity
In Paper, -
The tree growth-herbivory relationship depends on functional traits across forest biodiversity experiments
In Paper, -
Positive Diversity Effect on Woody Biomass Production by Promoting Cell Number and Cell Wall Thickness
In Paper, -
Trees suppress growth but sustain water consumption in response to flash drought in a subtropical forest
In Paper, -
Tree diversity, tree growth, and microclimate independently structure Lepidoptera herbivore community stability
In Paper, -
Cascading effects of tree diversity loss on herbivore-parasitoid interactions
In Paper, -
Within-individual leaf trait response to local light availability and biodiversity in a subtropical forest experiment
In Paper, -
Improving forest ecosystem functions by optimizing tree species spatial arrangement
In Paper, -
Bottom-up and top-down effects combine to drive predator-prey interactions in a forest biodiversity experiment
In Paper, -
Soil carbon sequestration: Facilitated effect of extrafloral nectary trees in a diverse subtropical forest
In Paper, -
Ecosystem consequences of functional diversity in forests and implications for restoration
In Paper, -
Enhanced plant diversity reduces nitrous oxide emissions in forest soils worldwide
In Paper, -
Tree species richness affects the trophic structure of soil oribatid mites via litter functional diversity and canopy cover: Evidence from stable isotope analysis (15N, 13C)
In Paper, -
Identifying seed families with high mixture performance in a subtropical forest biodiversity experiment
In Paper, -
Non- random tree species loss shifts soil fungal communities
In Paper, -
Understory shrub diversity: equally vital as overstory tree diversity to promote forest productivity
In Paper, -
Tree diversity increases forest temperature buffering via enhancing canopy density and structural diversity
In Paper, -
Multi-dimensionality of tree communities structure host-parasitoid networks and their phylogenetic composition
In Paper, -
Trait-based neighbourhood effects modulate the growth-weather relationships of subtropical trees
In Paper, -
Strong nestedness and turnover effects on stand productivity in a long‐term forest biodiversity experiment
In Paper, -
Plant diversity increases diversity and network complexity rather than alters community assembly processes of leaf-associated fungi in a subtropical forest
In Paper, -
Soil conditions modify species diversity effects on tree functional trait expression
In Paper, -
Plant diversity enhances ecosystem multifunctionality via multitrophic diversity
In Paper, -
Functional diversity of neighbours mediates sap flow density and radial growth of focal trees, but in different ways between evergreen and deciduous broadleaved species
In Paper, -
Mixed-species stands improve the coordination between leaf and fine root traits in a common garden experiment
In Paper, -
The spatial distribution of tree-tree interaction effects on soil microbial biomass and respiration
In Paper, -
Influence of tree mycorrhizal type, tree species identity, and diversity on forest root-associated mycobiomes
In Paper, -
Tree species diversity modulates the effects of fungal pathogens on litter decomposition: evidences from an incubation experiment
In Paper, -
Functional dissimilarity in mixed forests promotes stem radial growth by mitigating tree water deficit
In Paper, -
Tree and shrub richness modifies subtropical tree productivity by regulating the diversity and community composition of soil bacteria and archaea
In Paper, -
Systematic distributions of interaction strengths across tree interaction networks yield positive diversity–productivity relationships
In Paper, -
Plant–soil feedback is dependent on tree mycorrhizal types and tree species richness in a subtropical forest
In Paper, -
9 PhD positions in the field of forest biodiversity ecosystem functioning research (TreeDì / BEF-China)
In news, -
Multitrophic arthropod diversity mediates tree diversity effects on primary productivity
In Report, -
Tree communities and functional traits determine herbivore compositional turnover
In Paper, -
Within-individual leaf trait variation increases with phenotypic integration in a subtropical tree diversity experiment
In Paper, -
Subtropical forest tree genetic richness causes contrasting effects on soil fungal guilds in monocultures and mixed-species stands
In Paper, -
Carbon–biodiversity relationships in a highly diverse subtropical forest
In Paper, -
Functional potential of soil microbial communities and their subcommunities varies with tree mycorrhizal type and tree diversity
In Paper, -
Different assembly mechanisms of leaf epiphytic and endophytic bacterial communities underlie their higher diversity in more diverse forests
In Paper, -
Mycorrhizal Types Control Biodiversity Effects on Productivity
In Paper, -
Functional and phylogenetic relationships link predators to plant diversity via trophic and non-trophic pathways
In Paper, -
Tree species and genetic diversity increase productivity via functional diversity and trophic feedbacks
In Paper, -
Tree dissimilarity determines multi-dimensional beta-diversity of herbivores and carnivores via bottom-up effects
In Paper, -
Differential impacts on herbivore diversity and scale-dependence of tree diversity in subtropical forests
In Paper, -
Leaf nutritional content, tree richness, and season shape the caterpillar functional trait composition hosted by trees
In Paper, -
Species richness, functional traits and climate interactively affect tree survival in a large forest biodiversity experiment
In Paper, -
Effects of enemy exclusion on biodiversity–productivity relationships in a subtropical forest experiment
In Paper, -
Plants play stronger effects on soil fungal than bacterial communities and co-occurrence network structures in a subtropical tree diversity experiment
In Paper, -
Neighbourhood Species Richness Reduces Crown Asymmetry of Subtropical Trees in Sloping Terrain
In Paper, -
Niche partitioning in nitrogen uptake among subtropical tree species enhances biomass production
In Paper, -
Species richness stabilizes productivity via asynchrony and drought-tolerance diversity in a large-scale tree biodiversity experiment
In Paper, -
Planting new forests with high functional diversity helps improve productivity
In Paper, -
Special issue: Tree Diversity Effects on Ecosystem Functioning
In news, -
Understanding biodiversity in forests
In news, -
Phylogenetic relatedness, functional traits, and spatial scale determine herbivore co‐occurrence in a subtropical forest
In Paper, -
Tree species richness differentially affects the chemical composition of leaves, roots and root exudates in four subtropical tree species.
In Paper, -
Tree diversity and functional leaf traits drive herbivore-associated microbiomes in subtropical China.
In Paper, -
What shapes ground beetle assemblages in a tree species-rich subtropical forest?
In Paper, -
Soil fungi promote biodiversity–productivity relationships in experimental communities of young trees
In Paper, -
Plant and microbial pathways driving plant diversity effects on soil carbon accumulation in subtropical forest
In Paper, -
The significance of tree-tree interactions for forest ecosystem functioning
In Paper, -
Tree diversity and soil chemical properties drive the linkages between soil microbial community and ecosystem functioning
In Paper, -
Tree mycorrhizal type and tree diversity shape the forest soil microbiota
In Paper, -
Tree species richness promotes an early increase of stand structural complexity in young subtropical plantations
In Paper, -
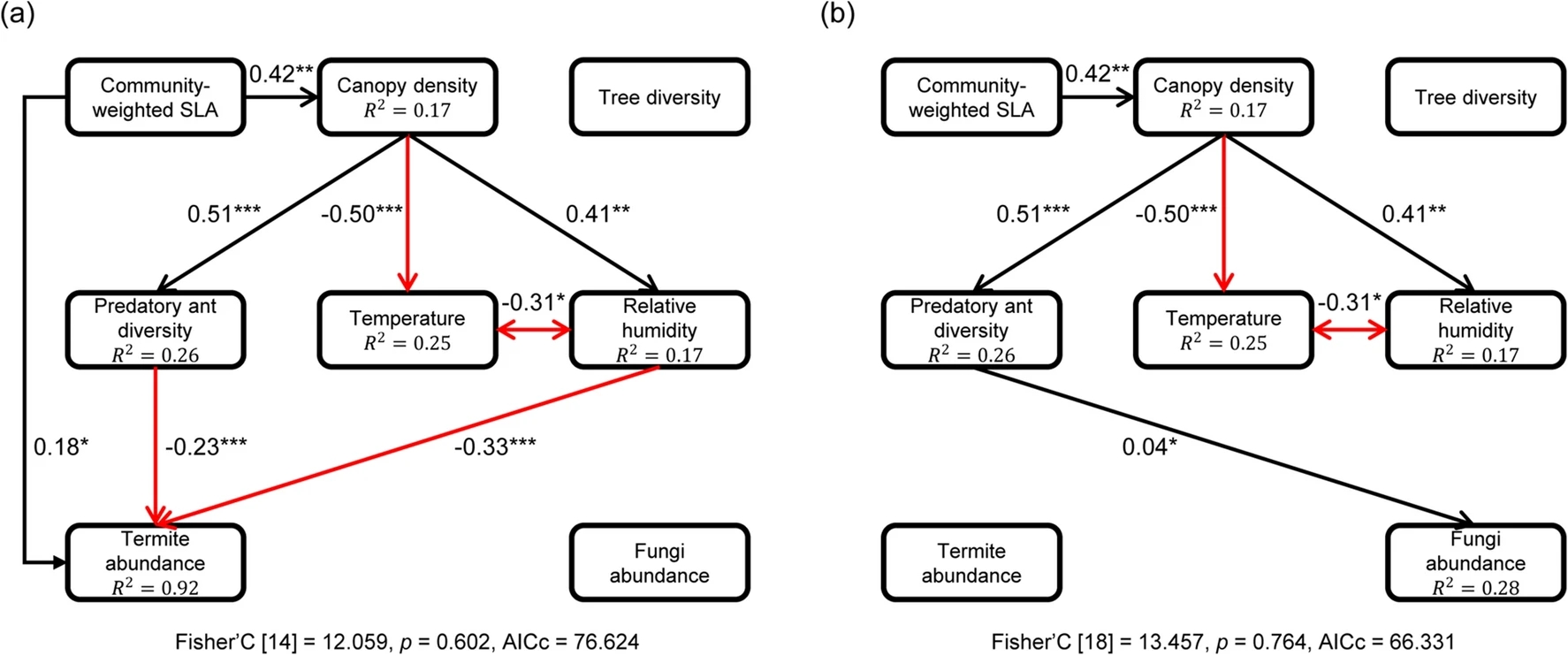
More diverse tree communities promote foliar fungal pathogen diversity, but decrease infestation rates per tree species, in a subtropical biodiversity experiment
In Paper, -
Local Tree Diversity Suppresses Foliar Fungal Infestation and Decreases Morphological but Not Molecular Richness in a Young Subtropical Forest
In Paper, -
Species identity and composition effects on community productivity in a subtropical forest
In Paper, -
Drivers of understorey biomass: tree species identity is more important than richness in a young forest
In Paper, -
Canopy Closure Retards Fine Wood Decomposition in Subtropical Regenerating Forests
In Paper, -
Plant identity strongly structures the root-associated fungal community in a diverse subtropical forest
In Paper, -
Radial growth response of trees to seasonal soil humidity in a subtropical forest
In Paper, -
Tree diversity promotes predatory wasps and parasitoids but not pollinator bees in a subtropical experimental forest
In Paper, -
Tree-tree interactions and crown complementarity: The role of functional diversity and branch traits for canopy packing
In Paper, -
Tree species richness modulates water supply in the local tree neighbourhood: evidence from wood δ13C signatures in a large-scale forest experiment
In Paper, -
9 PhD positions in forest biodiversity research within the International Research Training Group TreeDì (GRK 2324)
In News, -
Host functional and phylogenetic composition rather than host diversity structure plant-herbivore networks
In Paper, -
Genetic richness affects trait variation but not community productivity in a tree diversity experiment
In Paper, -
Neighbourhood diversity mitigates drought impacts on tree growth
In Paper, -
Growth-trait relationships depend on species richness in subtropical forest
In Paper, -
Neighbour species richness and local structural variability modulate aboveground allocation patterns and crown morphology of individual trees
In Paper, -
Herbivore phylogenetic diversity can be affected by plant diversity loss
In Paper, -
Multiple plant diversity components drive consumer communities across ecosystems
In Paper, -
Tree diversity increases robustness of multi-trophic interactions
In Paper, -
Species-rich forests store twice as much carbon as monocultures
In Paper, -
Species-rich forests better compensate environmental impacts
In Paper, -
Neighbourhood interactions drive overyielding in mixed-species tree communities
In Paper,