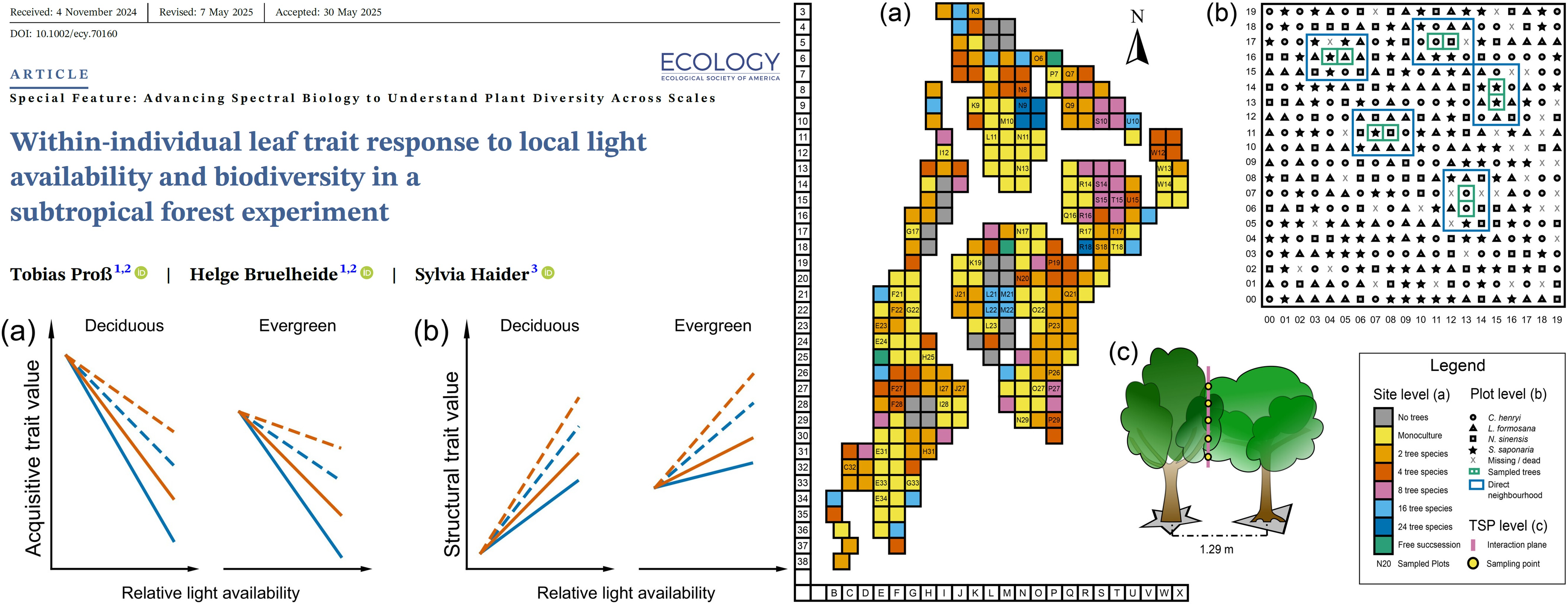
Leaf traits are important indicators of ecosystem functions. Trait values can vary widely between species, and a considerable amount of variation also occurs within species. However, within-individual variation is often neglected due to the limitations of traditional measurement tools. Many leaf trait values respond to light availability, which, in turn, is affected by the surrounding vegetation. Additionally, there is a strong within-individual light gradient, especially in tree canopies. In the BEF-China (Biodiversity–Ecosystem Functioning China) subtropical forest plantation, we analyzed how leaf trait values respond to light availability and neighboring tree species richness at the within-individual level. We sampled across the vertical light gradient formed by neighboring trees planted at varying diversity levels from monocultures to 24-species mixtures. We closely paired the leaf samples with sensor-based measurements of light availability. We used visible and near-infrared spectroscopy (spectral range: 350–2500 nm) to predict 14 leaf traits across 4981 leaves from 15 native tree species. Using a key feature of spectroscopy—deriving multiple leaf traits from a single spectral measurement of a sample—we assessed all traits simultaneously at the leaf level. We investigated whether an individual tree’s direct neighbor or the surrounding tree species richness had a stronger influence on the light–trait relationship. Most trait values responded to light availability, though this response differed between deciduous and evergreen species. We found that tree species richness and a tree’s direct neighbor could modify the light–trait relationship at the individual level. In some instances, a focal tree’s direct neighbor influenced its leaf trait values more than the tree species richness in its local neighborhood. Specifically, in conspecific tree pairs of evergreens, specific leaf area and leaf nitrogen displayed a stronger response to changing light conditions. This response to light availability suggests a mechanism for avoiding within-species competition that is observable at the within-individual level. Our results show that biodiversity influences ecosystem functions through its effects on within-individual leaf trait variation. The fact that the interplay between light availability, biodiversity, and leaf traits can be observed within-individual trees highlights the importance of within-individual leaf trait variation in biodiversity research.
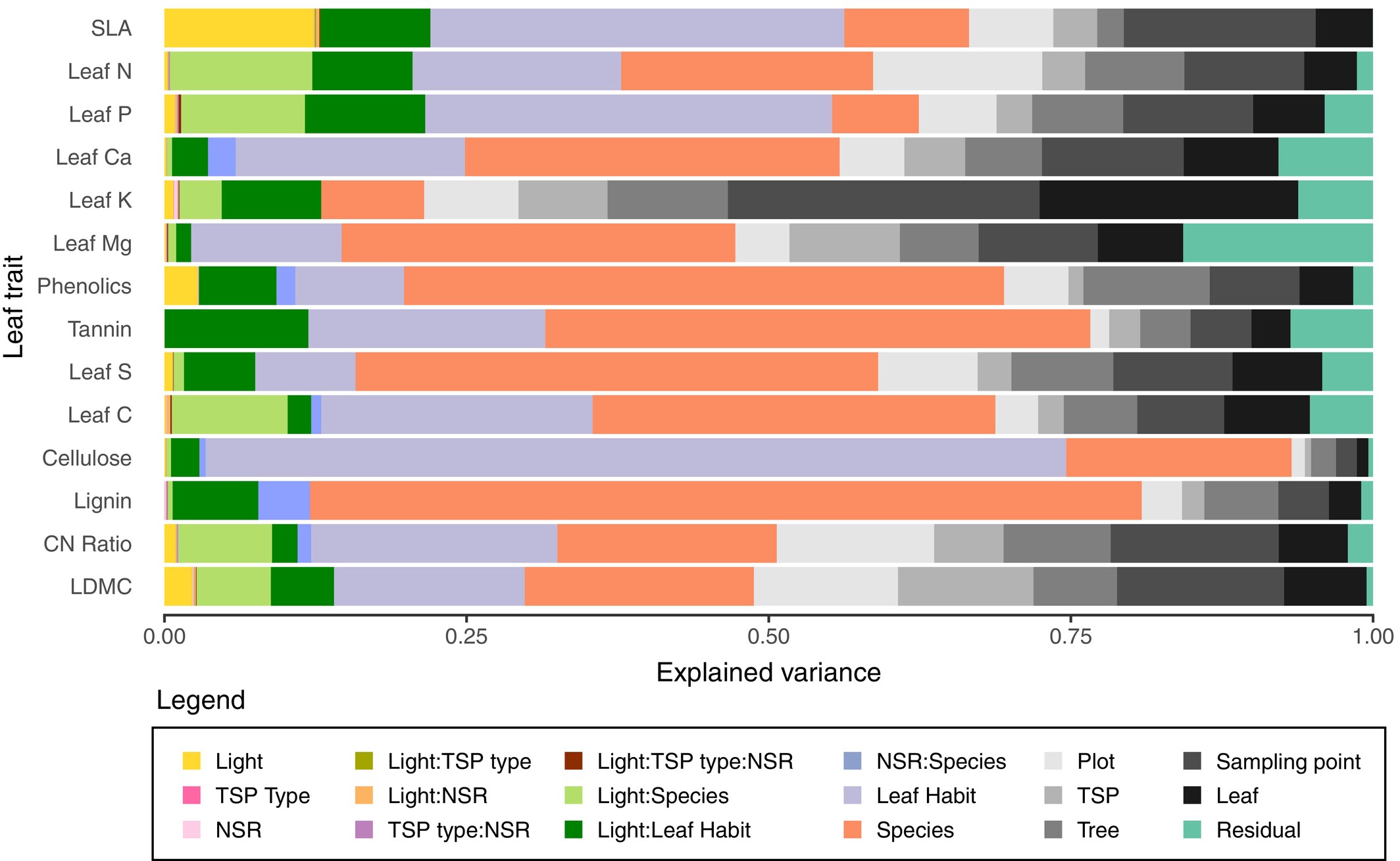
Figure 1. Proportions of explained variance for each leaf trait. Fixed effects include light, TSP type (tree species pair type), and NSR (neighborhood species richness), as well as all possible interactions (Light:TSP type, Light:NSR, TSP type:NSR, Light:TSP type:NSR).
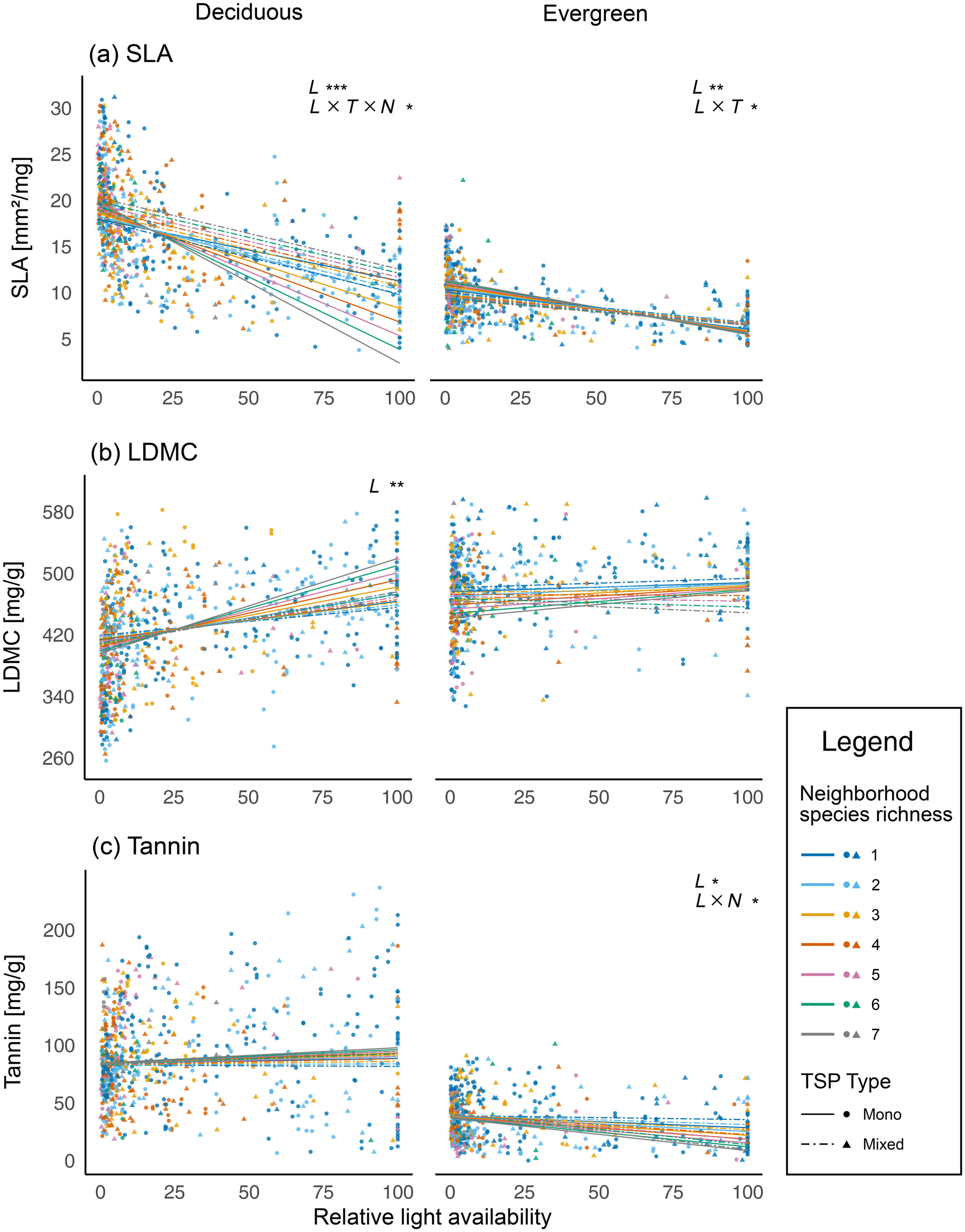
Figure 2. Leaf traits as functions of light availability, modified by TSP type (tree species pair type) and neighborhood species richness.
Literature:
Tobias Proß*, Helge Bruelheide, and Sylvia Haider. 2025. Within-individual leaf trait response to local light availability and biodiversity in a subtropical forest experiment. Ecology. 106(7):e70160. https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ecy.70160.