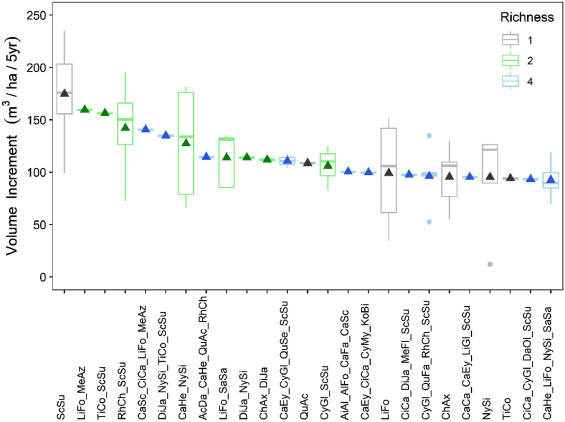
Biodiversity experiments have shown that high species richness increases productivity in forests. However, forests are diverse regarding community composition. It is unclear how species identity and species composition could contribute to the variation of productivity and how their effects interact with species richness. Here we used data from a 9-year-old planted forest experiment with 40 species to test the effects of species identity and species composition on productivity. The plots in the experiment were designed with various compositions across richness levels. We found that for the top 25 species compositions with the highest volume increment there were six monocultures (24%), eight 2-species mixtures (32%) and eleven 4-species mixtures (44%). Schima superba monoculture had the highest volume in the last study year and highest volume increment over five years, while 2-species and 4-species mixtures with Nyssa sinensis or Liquidambar formosana resultedinhighaverage above-ground volume accumulation. Most of the high-productivity species were deciduous with arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) associations. In addition, the percentage ofAM species in plots had a positive significant effect on both above-ground volume in 2018 and increment from 2013 to 2018. While the percentage of evergreen species showed no significant effect on above-ground volume increment, it did significantly decrease the above-ground volume in 2018. Overall, our results encourage reforestation management to consider species identity and species compositions of deciduous and/or AM species, such as Schima superba, Nyssa sinensis or Liquidambar formosana in the studied subtropical area, if the purpose is to enhance ecosystem productivity.
Literature:
Liwei Ma†, Franca J. Bongers†, Shan Li, Ting Tang, Bo Yang, Keping Ma and Xiaojuan Liu*. 2021. Species identity and composition effects on community productivity in a subtropical forest. Basic and Applied Ecology. 55: 87-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.baae.2021.01.005.