The coordination between leaf and root traits is conducive to an integrated understanding of whole-plant ecological strategies and reveals how community composition and diversity contribute to defining the functions and services of ecosystems. However, there is limited understanding regarding the impact of species richness and trait categories on the coordination between leaf and root traits.
Based on a 9-year common garden experiment, we investigated the leaf and fine root traits of 56 plots (25.8 m × 25.8 m) encompassing various trait categories (trait categories were defined according to the root depth, leaf habit, and mycorrhizal type) and different levels of species richness (1, 2, 4, 8) in the context of a forest biodiversity and ecosystem functioning experiment conducted in subtropical China (BEF-China).
We found the following: (1) Our findings indicate that there was generally a significant difference in leaf traits, occasionally in absorptive root traits, and no difference in transport root traits between different trait categories. (2) Conversely, species richness significantly influenced all transport root traits except root nitrogen and most leaf and absorptive root traits. (3) The results demonstrated that trait categories played a crucial role in the coordination between leaf and fine root traits. Additionally, the coordination between leaf and fine root traits increased with higher species richness, particularly in deep-rooted, evergreen, and ectomycorrhizal fungi species. Furthermore, the coordination between leaf and fine root traits was significantly lower in monocultures compared to four- and eight-species mixtures.
These results suggest that a significant mixture effect exists in the coordination between leaf and fine root traits due to the comprehensive and divergent capture of above- and belowground resources and reduced intraspecific competition. Therefore, compared to monocultures, mixed-species stands can enhance the coordination of leaf and fine root traits, and it is advisable to establish forests with mixtures of more than four species, dominated by deep-rooted, evergreen, and ectomycorrhizal fungi species, to maintain ecosystem stability and functional integrity.
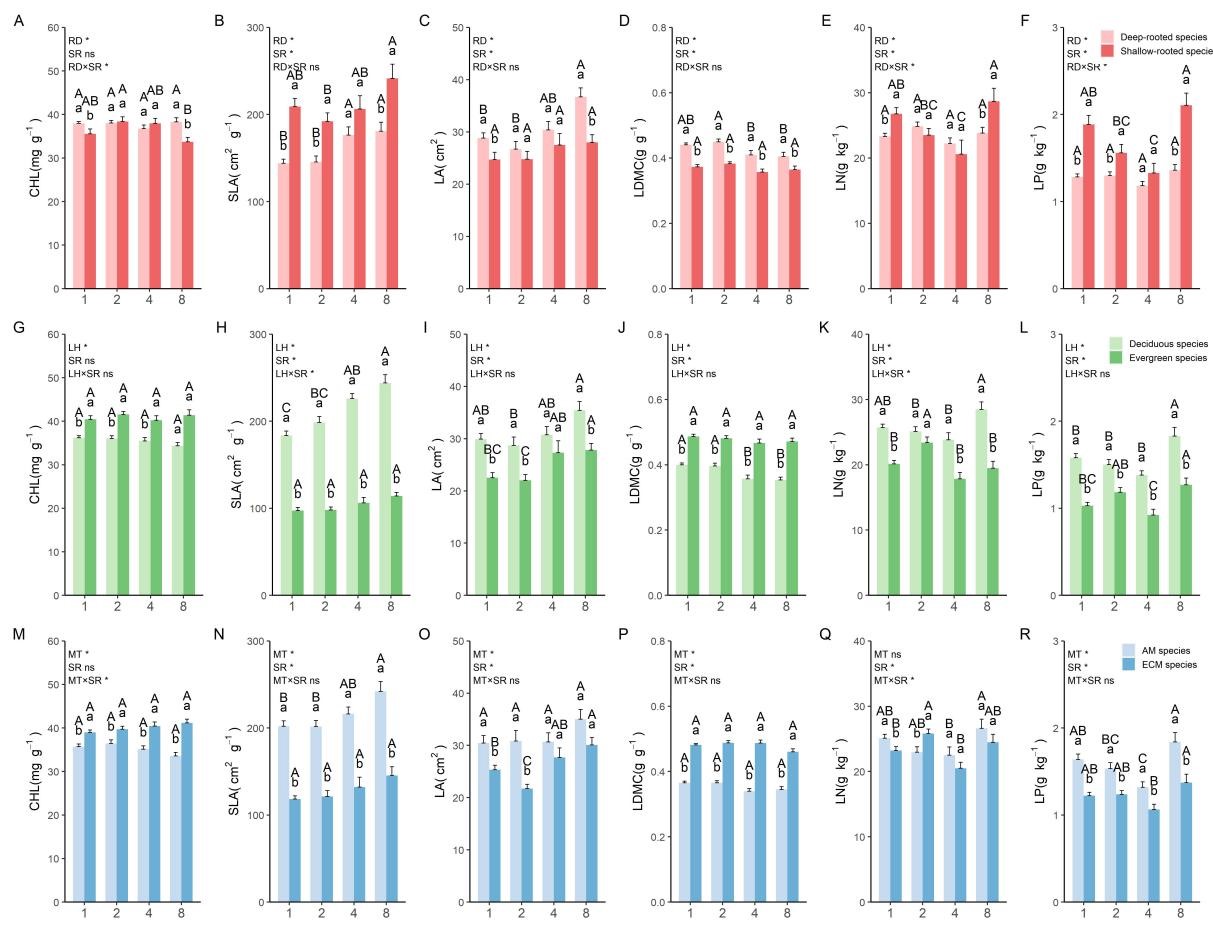
Figure 1. Variations in the CHL (A), SLA (B), LA (C), LDMC (D), LN (E) and LP (F) for root deep-rooted and shallow-rooted species; Variations in the CHL (G), SLA (H), LA (I), LDMC (J), LN (K) and LP (L) for deciduous and evergreen species; Variations in the CHL (M), SLA (N), LA (O), LDMC (P), LN (Q) and LP (R) for AM and ECM species.
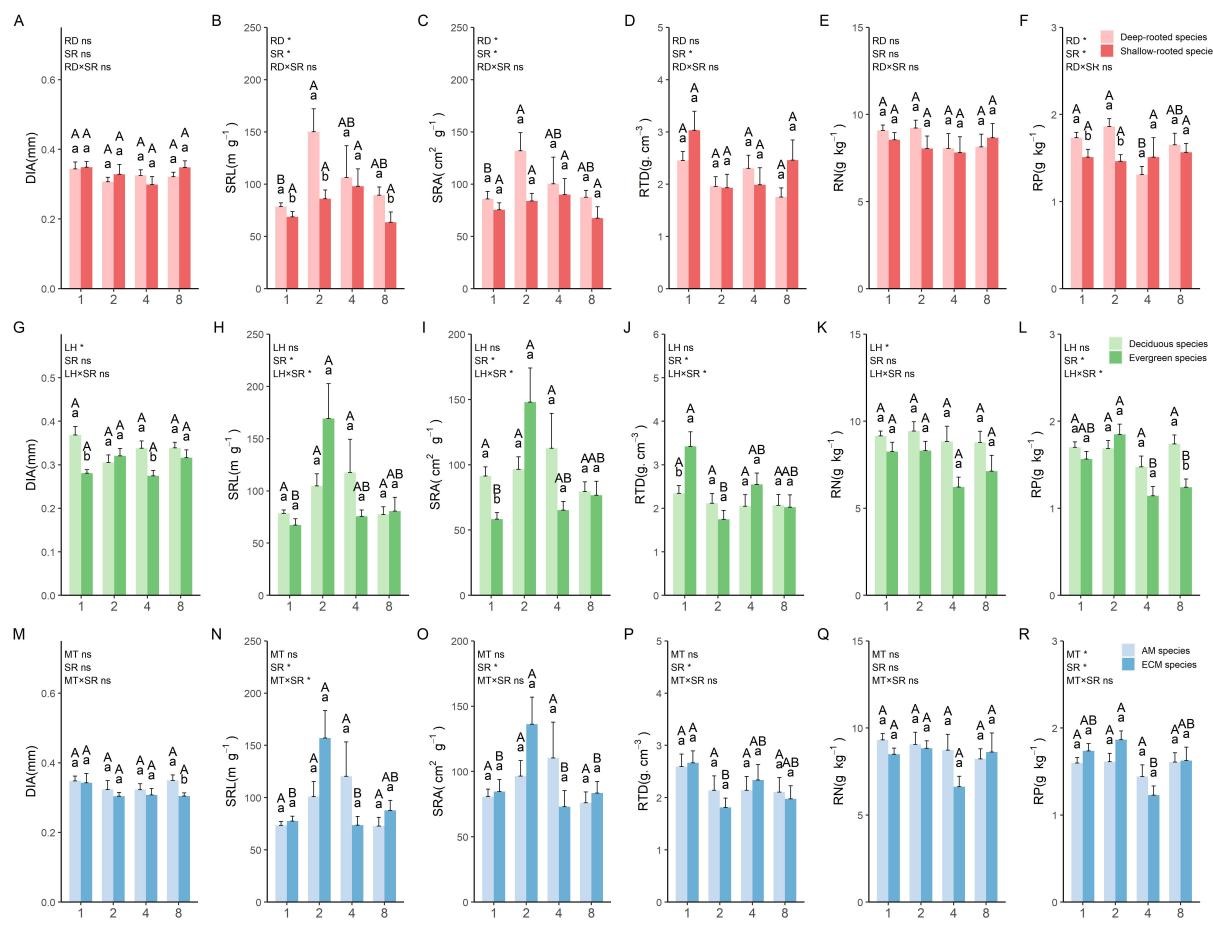
Figure 2. Variations in the DIA (A),SRL (B), SRA (C), RTD (D), RN (E) and RP (F) of absorptive roots for root deep-rooted and shallow-rooted species; Variations in the DIA (G), SRL (H), SRA (I), RTD (J), RN (K) and RP (L) of absorptive roots for deciduous and evergreen species; Variations in the DIA (M), SRL (N), SRA (O), RTD (P), RN (Q) and RP (R) of absorptive roots for AM and ECM species.
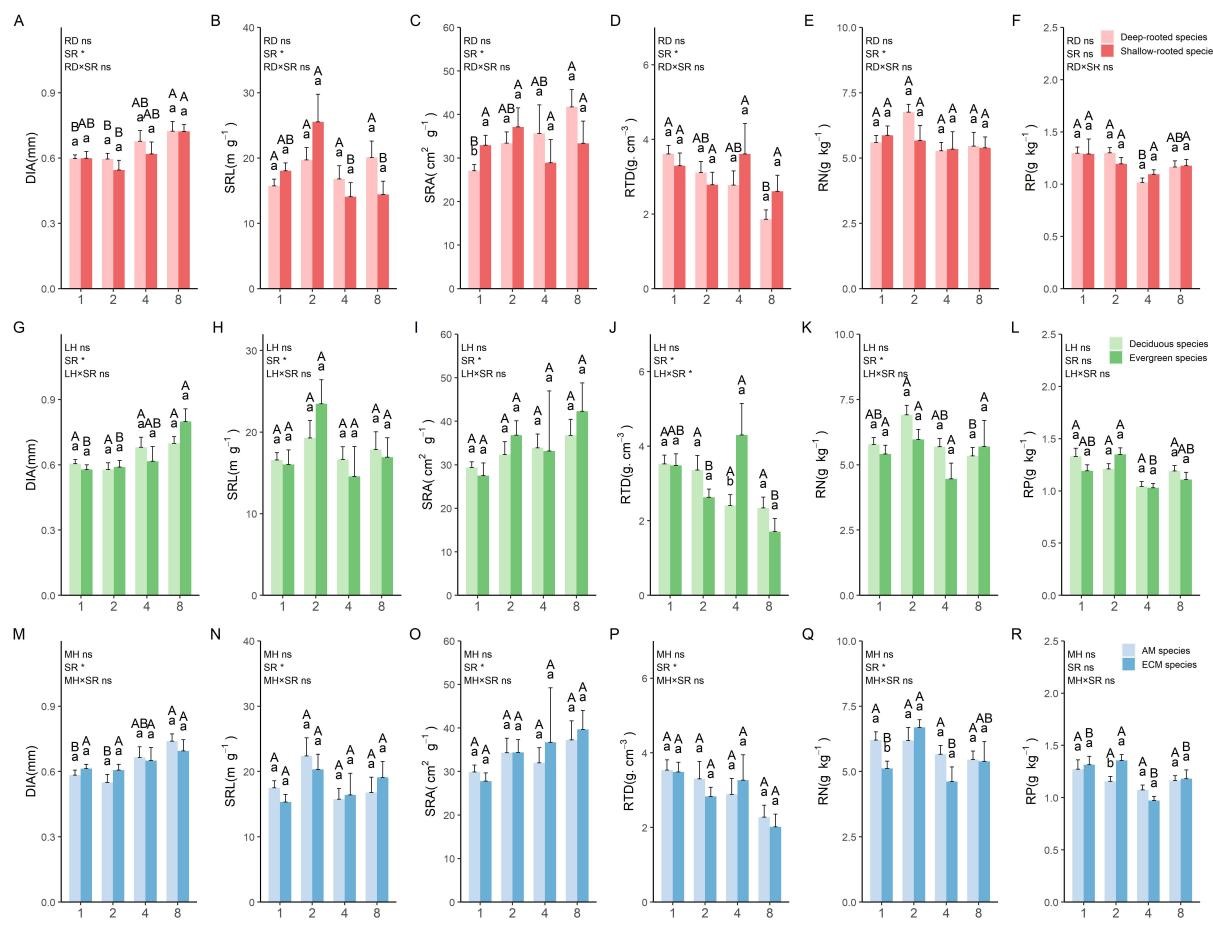
Figure 3. Variations in the DIA (A),SRL (B), SRA (C), RTD (D), RN (E) and RP (F) of transport roots for root deep-rooted and shallow-rooted species; Variations in the DIA (G), SRL (H), SRA (I), RTD (J), RN (K) and RP (L) of transport roots for deciduous and evergreen species; Variations in the DIA (M), SRL (N), SRA (O), RTD (P), RN (Q) and RP (R) of transport roots for AM and ECM species.
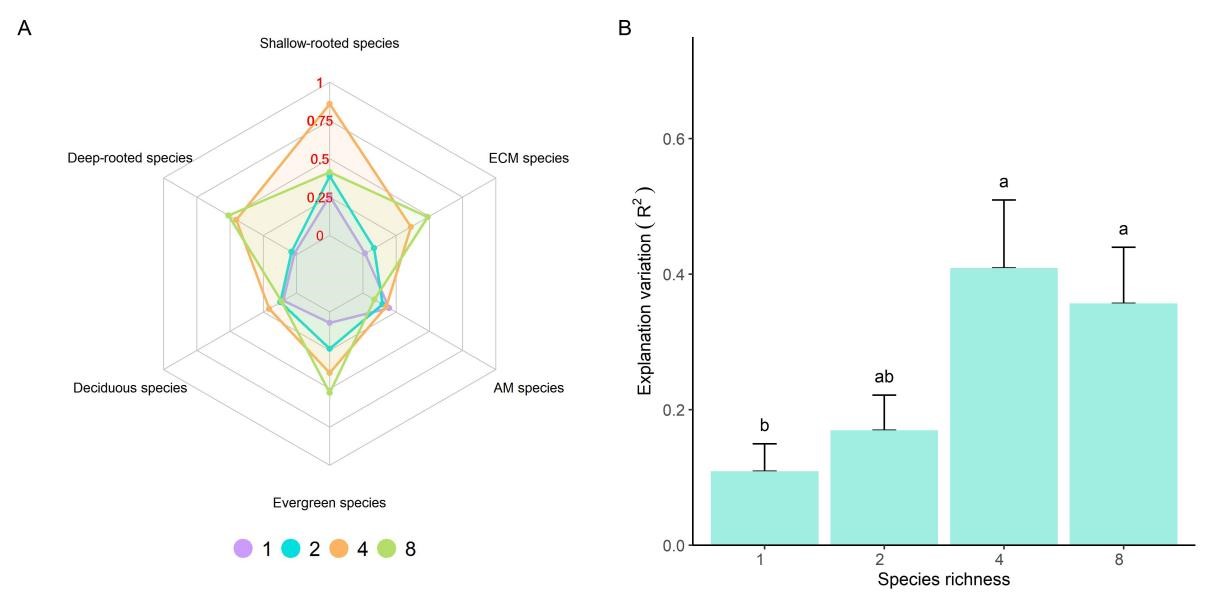
Figure 4. Radar plot of the coordination between leaf and fine root traits across different trait categories at different species richness levels (A) and the average explained variation across different tree species richness levels (B).
Literature:
Yuxin Li#, Cancan Zhang#, Yiqing Cheng, Shiqi Zeng, Shiyun Yang, Xiaofan Lin, Jianmin Shi*, Wensheng Bu*. 2024. Mixed-Species Stands Improve the Coordination between Leaf and Fine Root Traits in a Common Garden Experiment. Forests. 15(5): 744. http://doi.org/10.3390/f15050744.

