The capacity of forests to sequester carbon in both above- and belowground compartments is a crucial tool to mitigate rising atmospheric carbon concentrations. Belowground carbon storage in forests is strongly linked to soil microbial communities that are the key drivers of soil heterotrophic respiration, organic matter decomposition and thus nutrient cycling. However, the relationships between tree diversity and soil microbial properties such as biomass and respiration remain unclear with inconsistent findings among studies. It is unknown so far how the spatial configuration and soil depth affect the relationship between tree richness and microbial properties.
Here, we studied the spatial distribution of soil microbial properties in the context of a tree diversity experiment by measuring soil microbial biomass and respiration in subtropical forests (BEF-China experiment). We sampled soil cores at two depths at five locations along a spatial transect between the trees in mono- and hetero- specific tree pairs of the native deciduous species Liquidambar formosana and Sapindus saponaria.
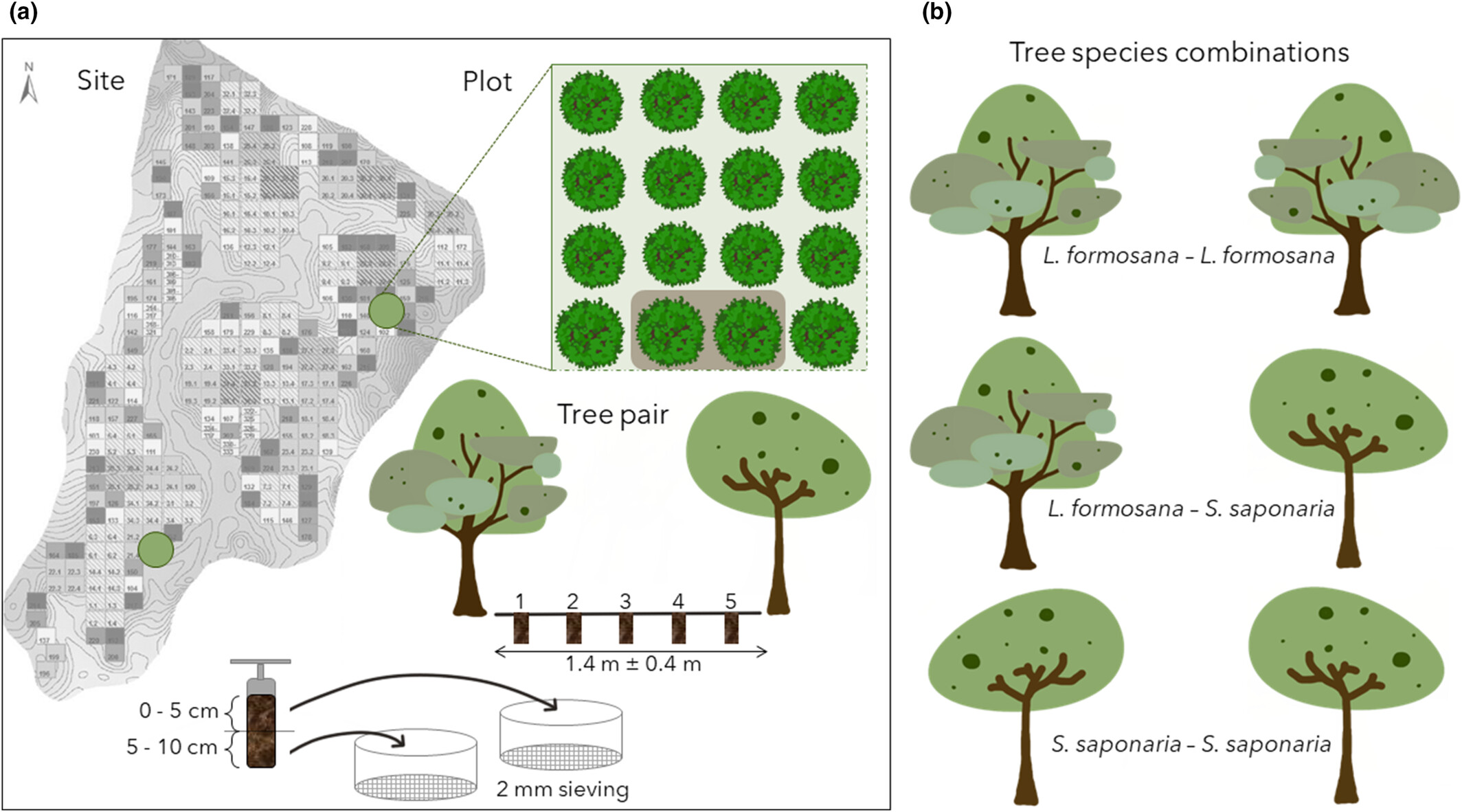
Figure 1. Sampling Design. Overview of the BEF-China experimental Site a (Panel a) with the two sampled plots (green) representing two-species mixture plots. Plot tree planting grid pattern with a marked tree pair, here only a small section of the 20 × 20 trees plot was drawn.
Our analyses showed decreasing soil microbial biomass and respiration with increasing soil depth and distance from the tree in mono-specific tree pairs. We calculated belowground overyielding of soil microbial biomass and respiration – which is higher microbial biomass or respiration than expected from the monocultures – and analysed the distribution patterns along the transect. We found no general overyielding across all sampling positions and depths. Yet, we encountered a spatial pattern of microbial overyielding with a significant microbial overyielding close to L. formosana trees and microbial underyielding close to S. saponaria trees. We found similar spatial patterns across microbial properties and depths that only differed in the strength of their effects.
Our results highlight the importance of small-scale variations of tree–tree interaction effects on soil microbial communities and functions and are calling for better integration of within- plot variability to understand biodiversity–ecosystem functioning relationships.
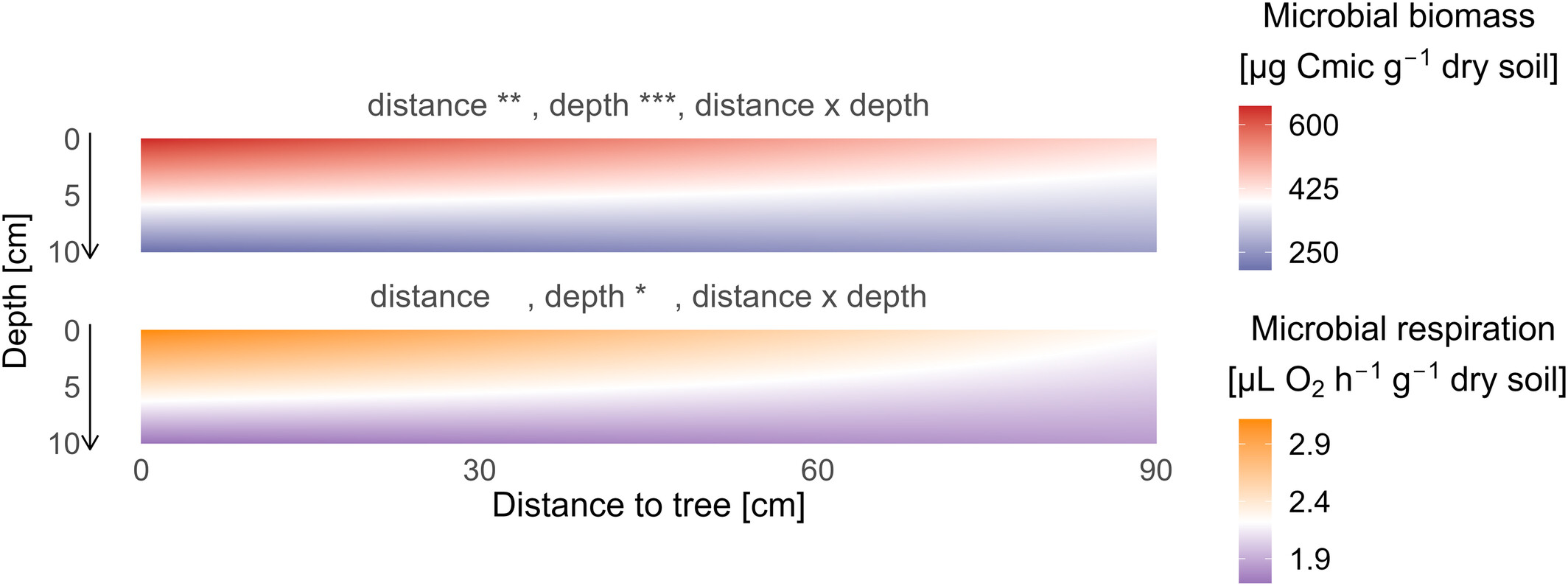
Figure 2. Distance to tree and depth effects on microbial biomass (top) and respiration (bottom) in mono-specific tree pairs. Effects are predicted from the model (soil properties ~ depth × distance to tree) with plot as random effect. Distance to tree reports the distance to the closest tree from mono-specific tree pairs. Microbial biomass is coloured blue (low) to red (high), and microbial respiration is coloured purple (low) to orange (high).
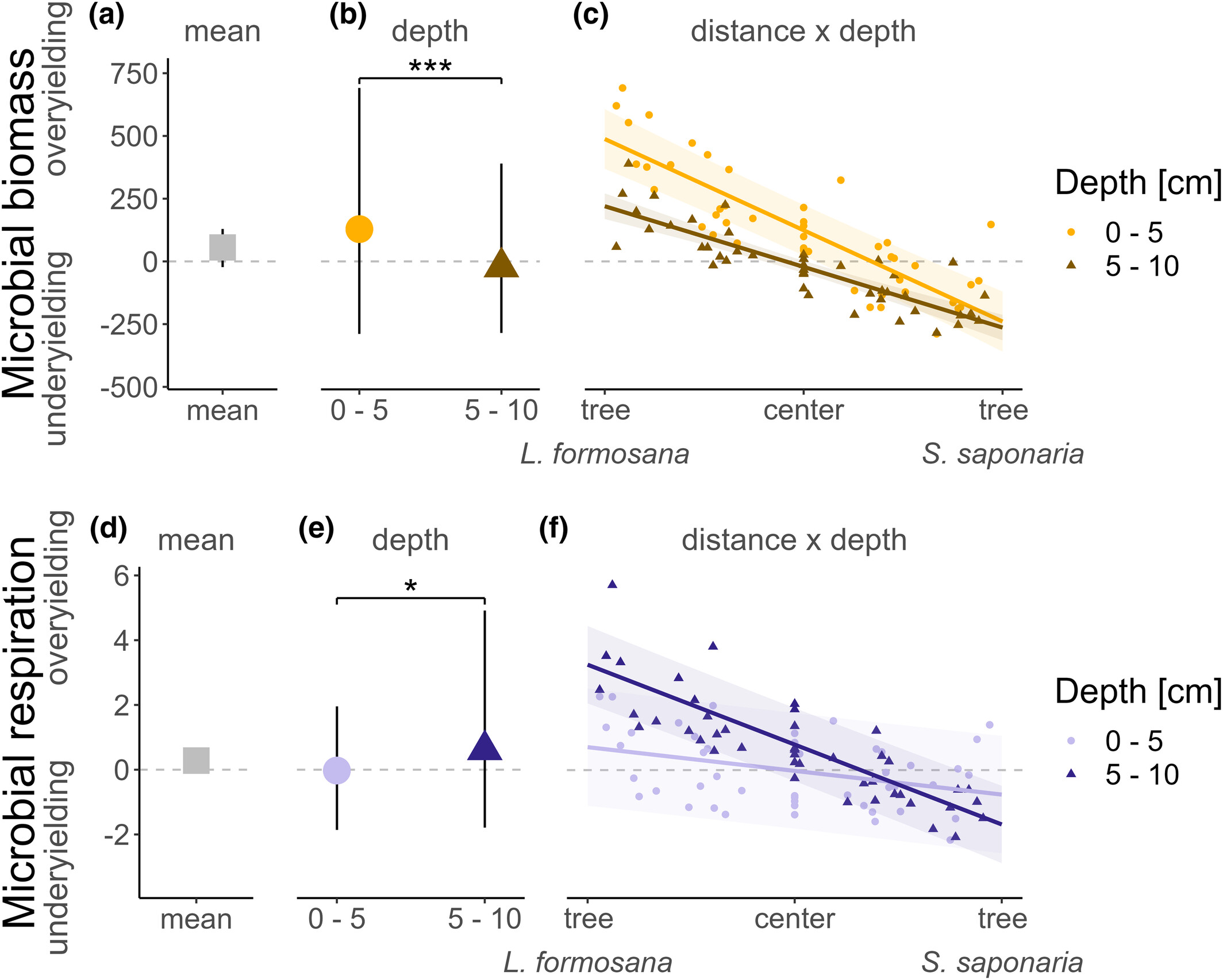
Figure 3. Distance to tree and depth effects on microbial biomass (top) and respiration (bottom) overyielding in hetero-specific tree pairs. The mean value (grey square) of overyielding for microbial biomass (a) and respiration (d) across all depths and positions, for each depth (microbial biomass: b, yellow circle for 0–5 cm; brown triangle for 5–10 cm, and microbial respiration: e, light blue circle for 0–5 cm; dark blue triangle for 5–10 cm) and each sampling point by depth (microbial biomass: C and respiration: f). Confidence intervals were predicted from models using the ‘ggpredict’ function of the R package ggeffects. The significance levels were standardised across the panels (*p < .05; ***p < .001).
Literature:
Henriette Christel*, Helge Bruelheide, Simone Cesarz, Nico Eisenhauer, Georg J A Hahn, Remy Beugnon. 2024. The spatial distribution of tree-tree interaction effects on soil microbial biomass and respiration. Ecology and Evolution. 14(6): e11530. http://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.11530.